seq2seq,RNN中的多进多出
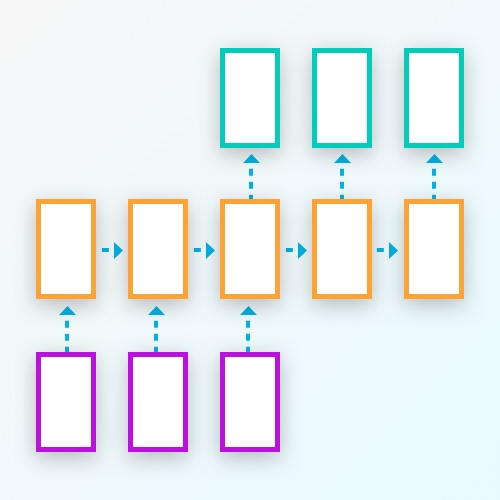
seq2seq,即往神经网络输入一个序列,然后神经网络处理完整个序列之后再返回一个序列.上图中,一个紫色方块代表一个单元输入,一个橙色方块代表一个RNN网络,一个绿色方块代表一个单元输出.这是RNN众多使用方式中的一种.可以用来做翻译,比如,输入一个完整的中文句子,然后可以得到一句对应的英文翻译.做概括,输入一段文字,然后可以得到一个话的总结.还可以做视频描述,把视频的每一帧图片作为输入,然后可以返回一个话描述视频的场景.
使用tensorflow实现seq2seq的步骤和代码
下面会介绍搭建seq2seq网络的关键代码,如果想看完整的代码,可以查看这里(搭建简单的seq2seq,网络可以按照字母表顺序,给输入的序列重新排序)
构建网络的伪代码:
1.编码器
* 输入向量化
* 解码器单元
2.解码器
a - 预处理解码器输入
b - 搭建解码器
* 输入向量化
* 解码器单元
* 全链接输出层
* 训练用的解码器
* 预测用的解码器
3. Seq2seq 模型 -> 编码器 + 解码器
4. 使用优化器训练模型
编码器
构建模型首先需要有一个编码器,我们首先需要把输入转化成向量,然后构建编码器,把向量化的数据输入到编码器. (输入转化成向量有两种情况,图片类输入可以通过CNN提取图片特征向量,文字类也是需要用向量表示,具体原因请查看word2vec相关文章)
这里的输入是一串字母
- 使用
tf.contrib.layers.embed_sequence把输入转化成向量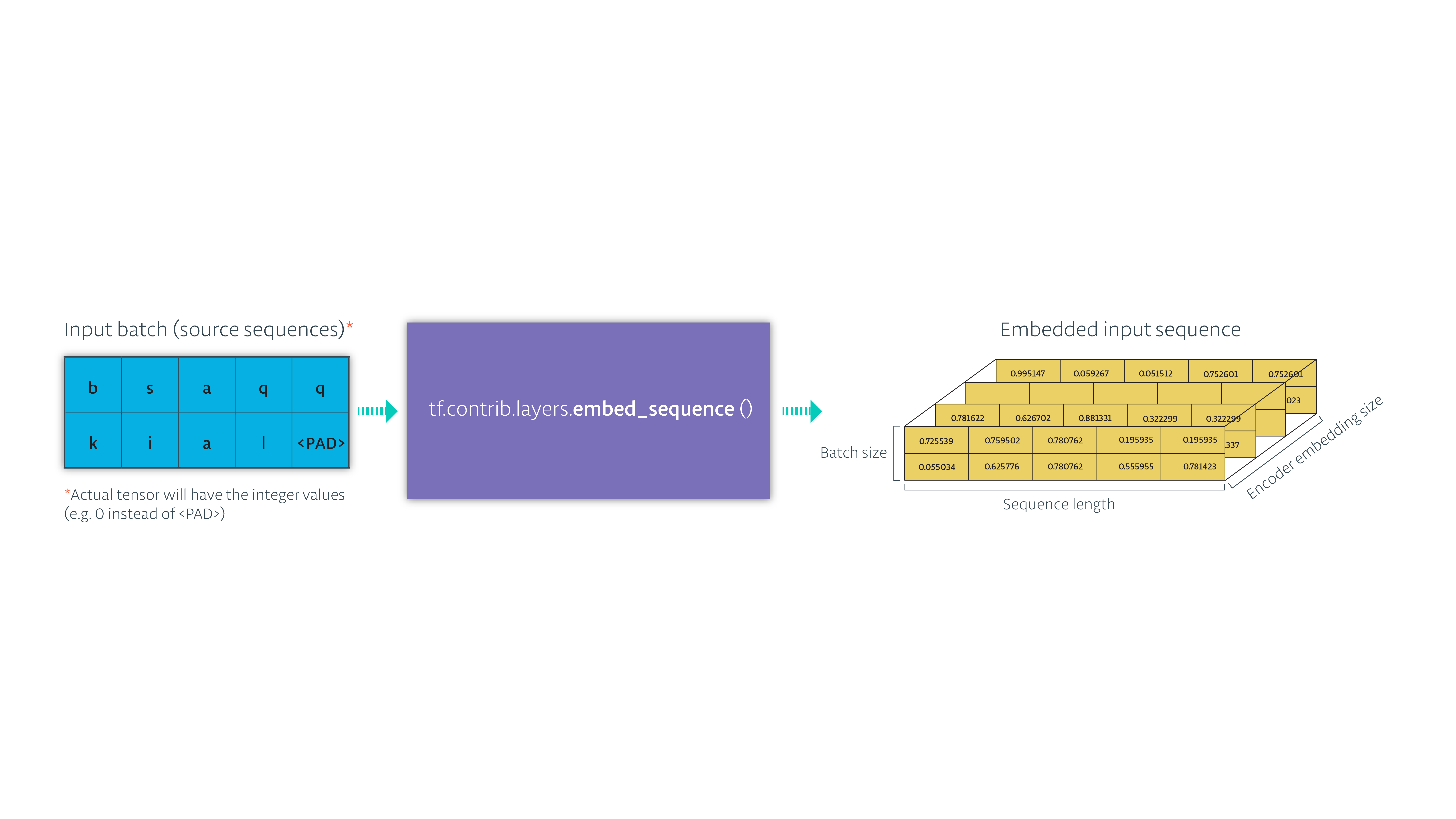
- 把向量化的数据传给RNN,保存RNN的状态,忽略输出
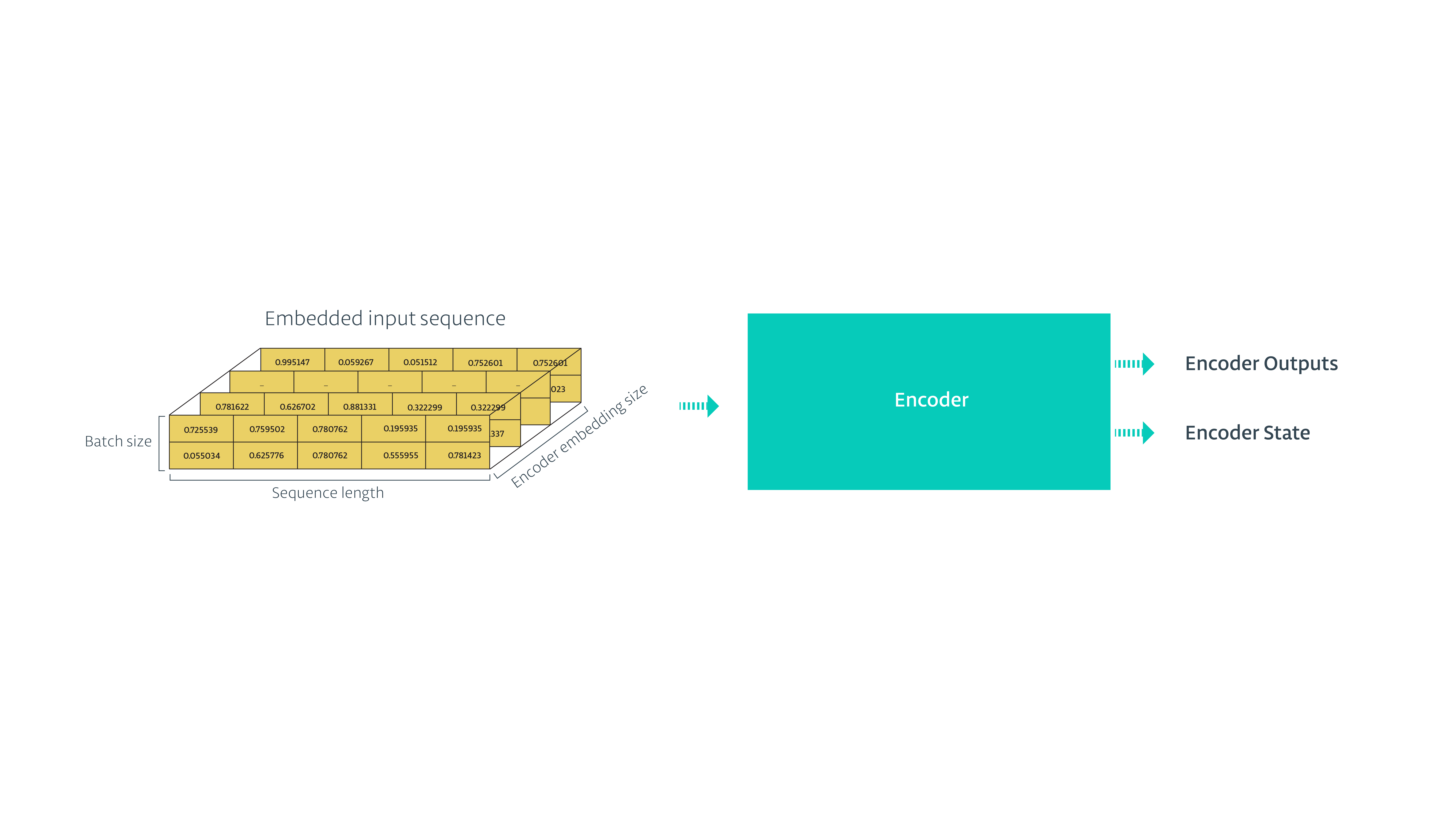 具体代码如下:
具体代码如下:
def encoding_layer(input_data, rnn_size, num_layers, source_sequence_length, source_vocab_size, encoding_embedding_size): # Encoder embedding # 把输入转化成向量 enc_embed_input = tf.contrib.layers.embed_sequence(input_data, source_vocab_size, encoding_embedding_size) # RNN cell def make_cell(rnn_size): enc_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size, initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2)) return enc_cell enc_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([make_cell(rnn_size) for _ in range(num_layers)]) enc_output, enc_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(enc_cell, enc_embed_input, sequence_length=source_sequence_length, dtype=tf.float32) return enc_output, enc_state
解码器
解码器可能是这个模型中最复杂的一部分. 我们将按下面的步骤来构建:
- 预处理解码器输入
- 搭建解码器
- 输入向量化
- 解码器单元
- 全链接输出层
- 训练用的解码器
- 预测用的解码器
预处理解码器的输入
在训练过程中,目标序列会在两个地方被使用到:
- 使用它们来计算模型的损失
- 把它们作为解码器的输入,以让模型更加健壮
现在我们需要来看一下第二点.让我们假设我们的目标序列看起来像这样:
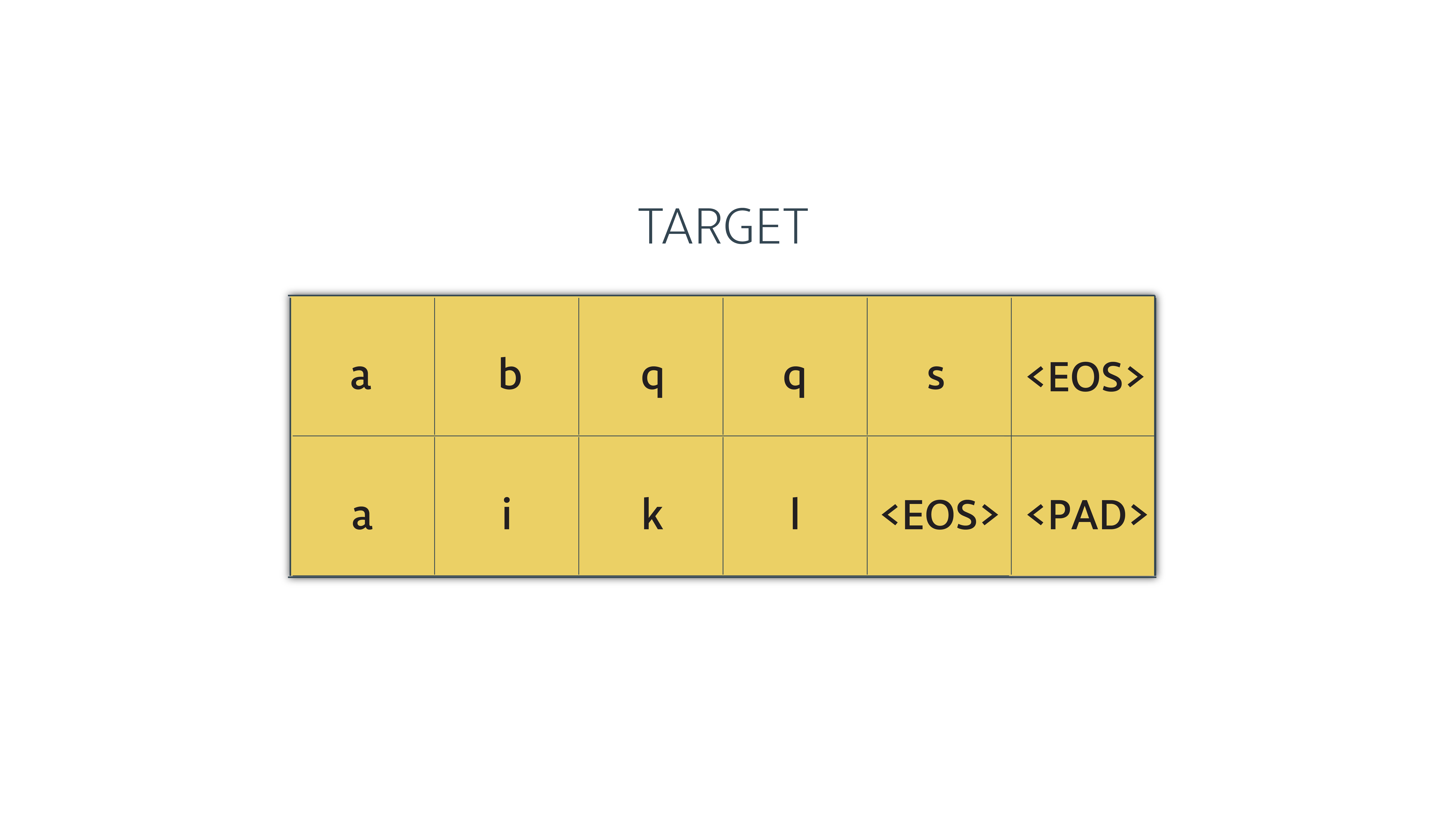
在我们把它喂给解码器之前需要做一个简单的变换:
-
每次我们需要把序列中的一项喂给解码器.想一下最后一步 – 当解码器输出它的输出的最后一项.那一步的输入是目标序列的倒数第二个.解码器在这个场景没有使用目标序列的最后一项.所以,我们将移除最后一项.
这个我们可以通过 tensorflow 的 tf.strided_slice() 来实现. 我们将输入一个张量还有开始和结束的位置,来对数据进行裁剪
-
我们要喂给解码器的序列中的第一项必须是 GO , 所以我们把它加在开始的位置
 现在这个张量已经可以喂给解码器了,它看上去像这样:
现在这个张量已经可以喂给解码器了,它看上去像这样:
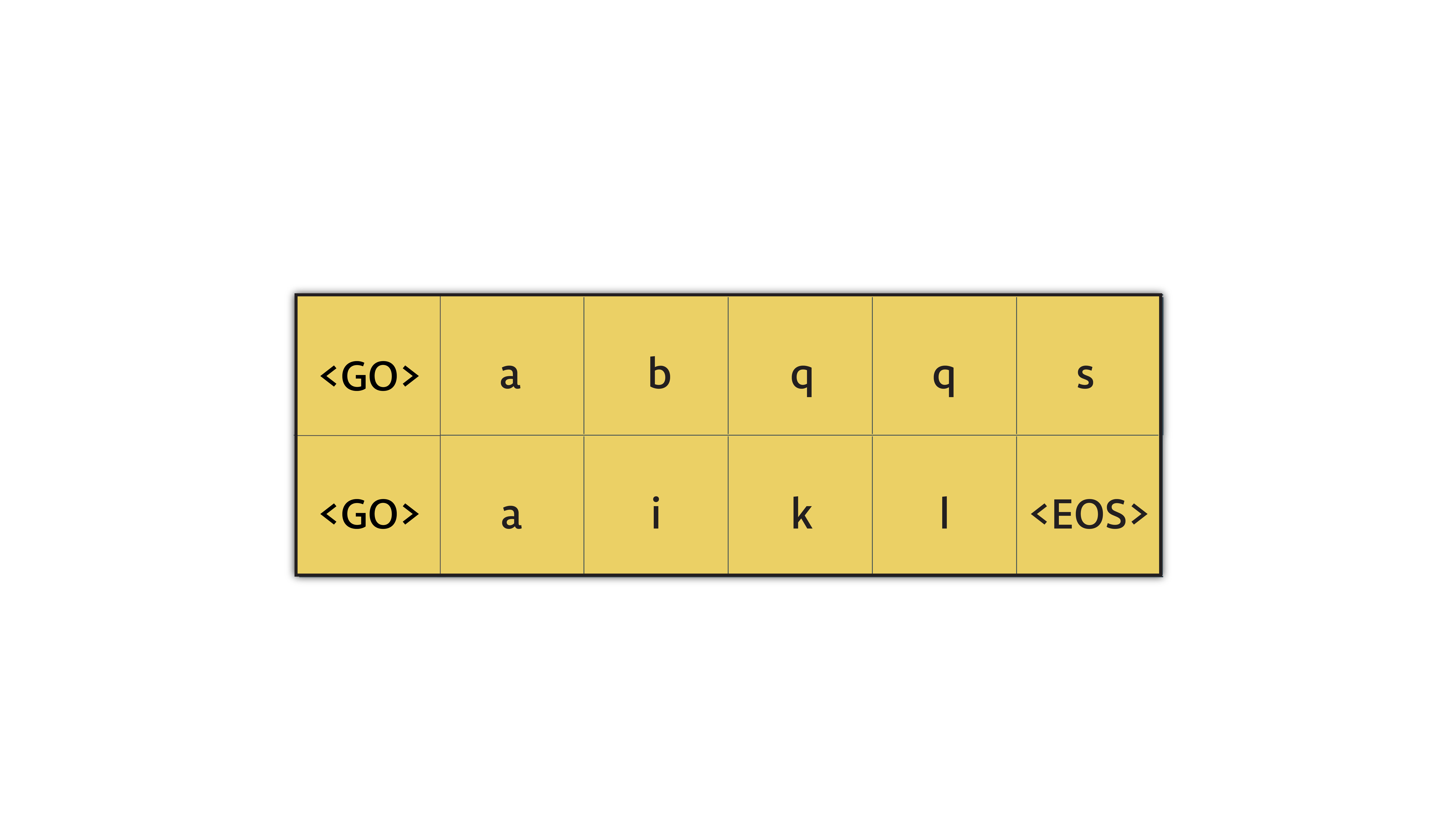
代码如下:
# Process the input we'll feed to the decoder
def process_decoder_input(target_data, vocab_to_int, batch_size):
'''Remove the last word id from each batch and concat the <GO> to the begining of each batch'''
ending = tf.strided_slice(target_data, [0, 0], [batch_size, -1], [1, 1])
dec_input = tf.concat([tf.fill([batch_size, 1], vocab_to_int['<GO>']), ending], 1)
return dec_input
构建解码器的成员
- 向量化
- 解码器单元
- 全链接层
- 训练用的解码器
- 预测用的解码器
-
向量化 现在我们已准备好了要喂给训练用的解码器的数据, 我们需要把它向量化,这样我们才能喂给解码器.
我们将构建一个类似下图的向量化矩阵,然后使用 tf.nn.embedding_lookup 在矩阵中查找对应的向量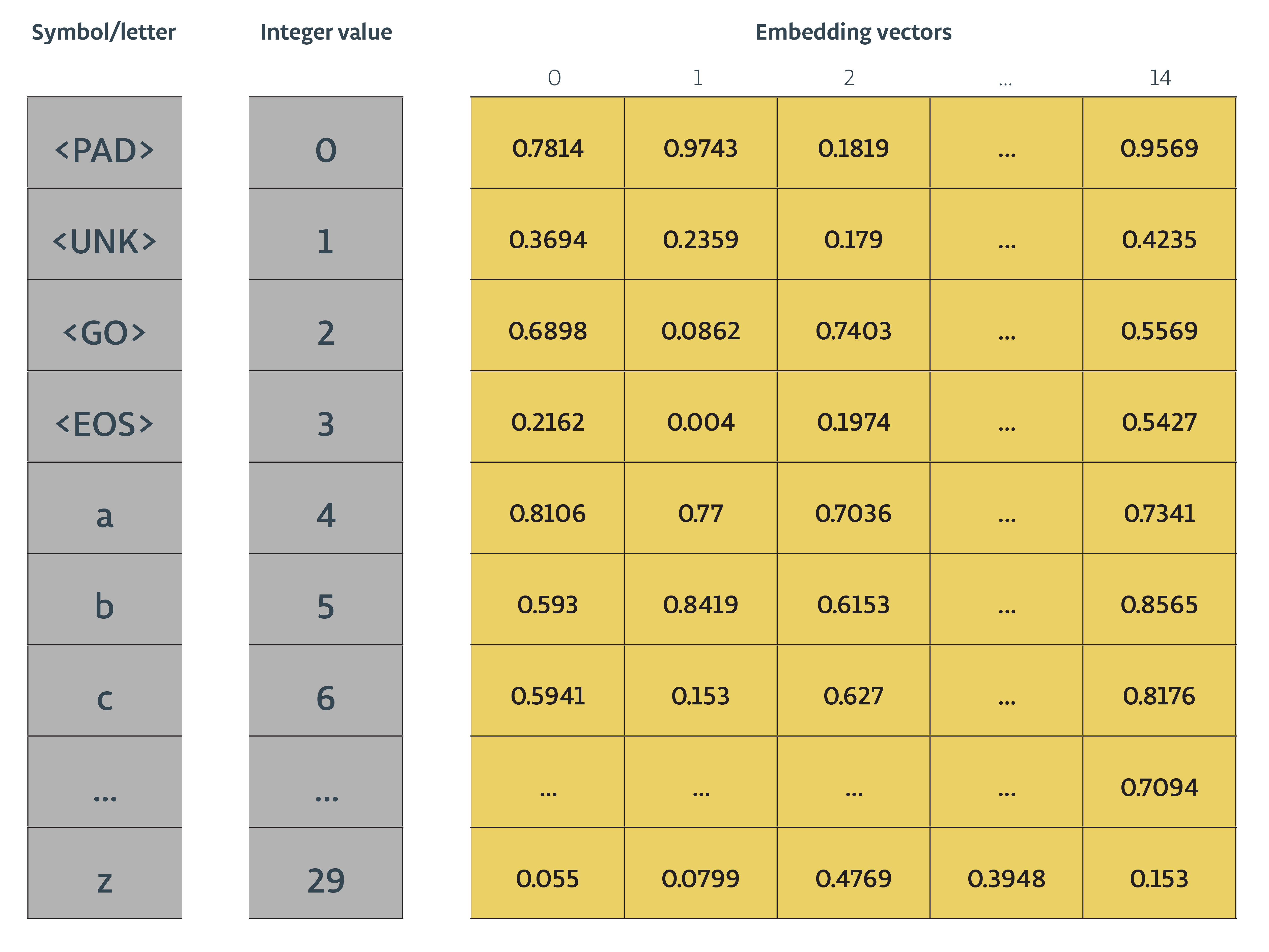
-
解码器单元 然后我们将创建解码器单元. 和编码器一样,这里也会用 tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell. 我们需要创建一个训练用的解码器,还有一个预测用的解码器.这两个解码器会共享一套参数
-
全链接输出层 在我们声明解码器之前,我们需要声明一个输出层,它是一个 tensorflow.python.layers.core.Dense 层,把解码器的输出转化成解码器输出每个词对应的概率.
-
训练用的解码器 本质上,我们将构建两个共享一套参数的解码器.一个用来训练,一个用来预测.这个模型的共同点是都是使用 tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder 和 tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode 来构建.区别在于我们把目标序列作为训练用的解码器的输入,让它更有鲁棒性. 我们可以想象一下训练用的模型
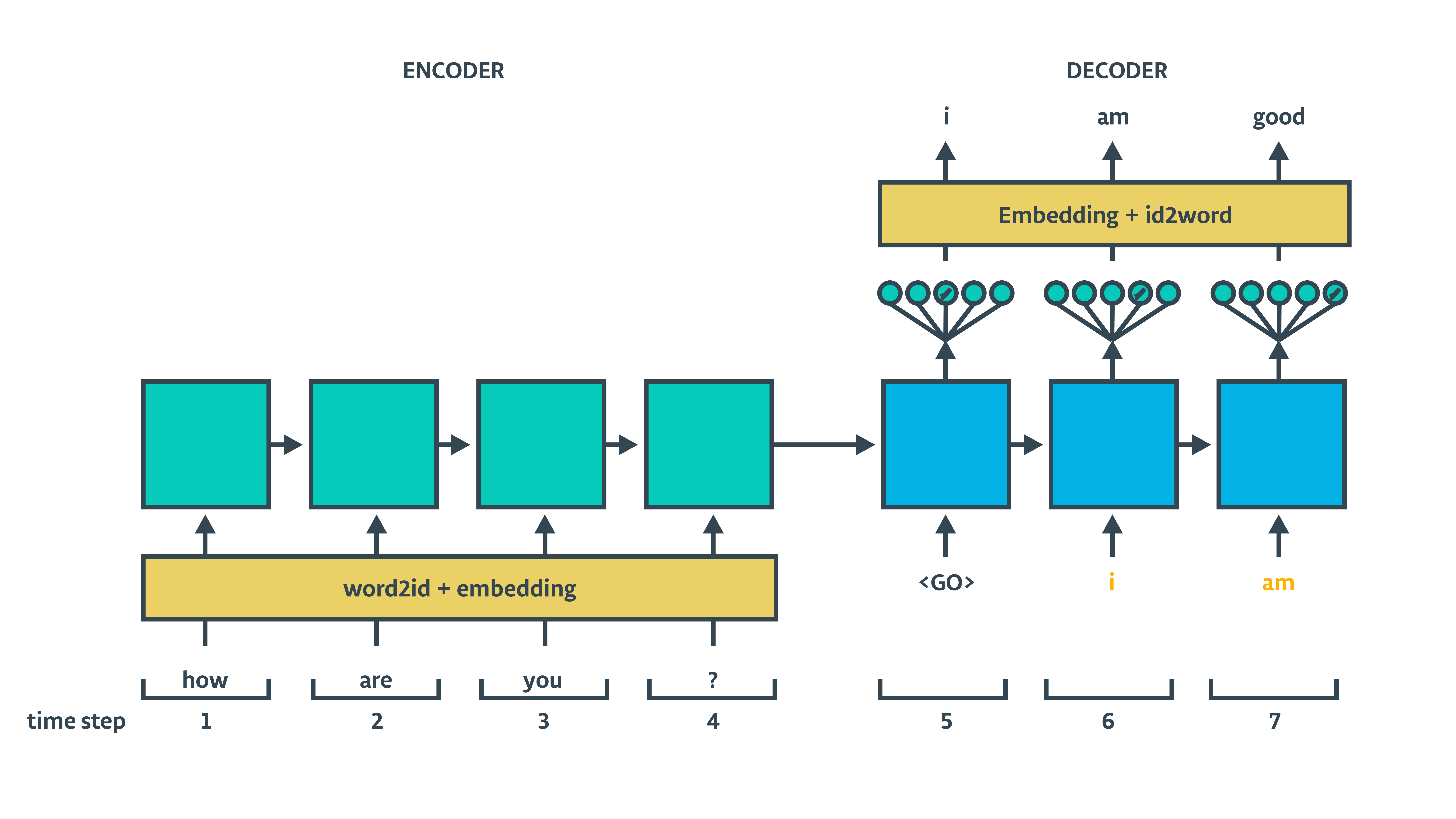 训练用的解码器没有把上一单元输出作为下一个输入.取而代之的是,输入训练集的目标序列.(橙色的单词)
训练用的解码器没有把上一单元输出作为下一个输入.取而代之的是,输入训练集的目标序列.(橙色的单词) -
预测用的解码器 预测用的解码器就是我们真正需要使用的模型
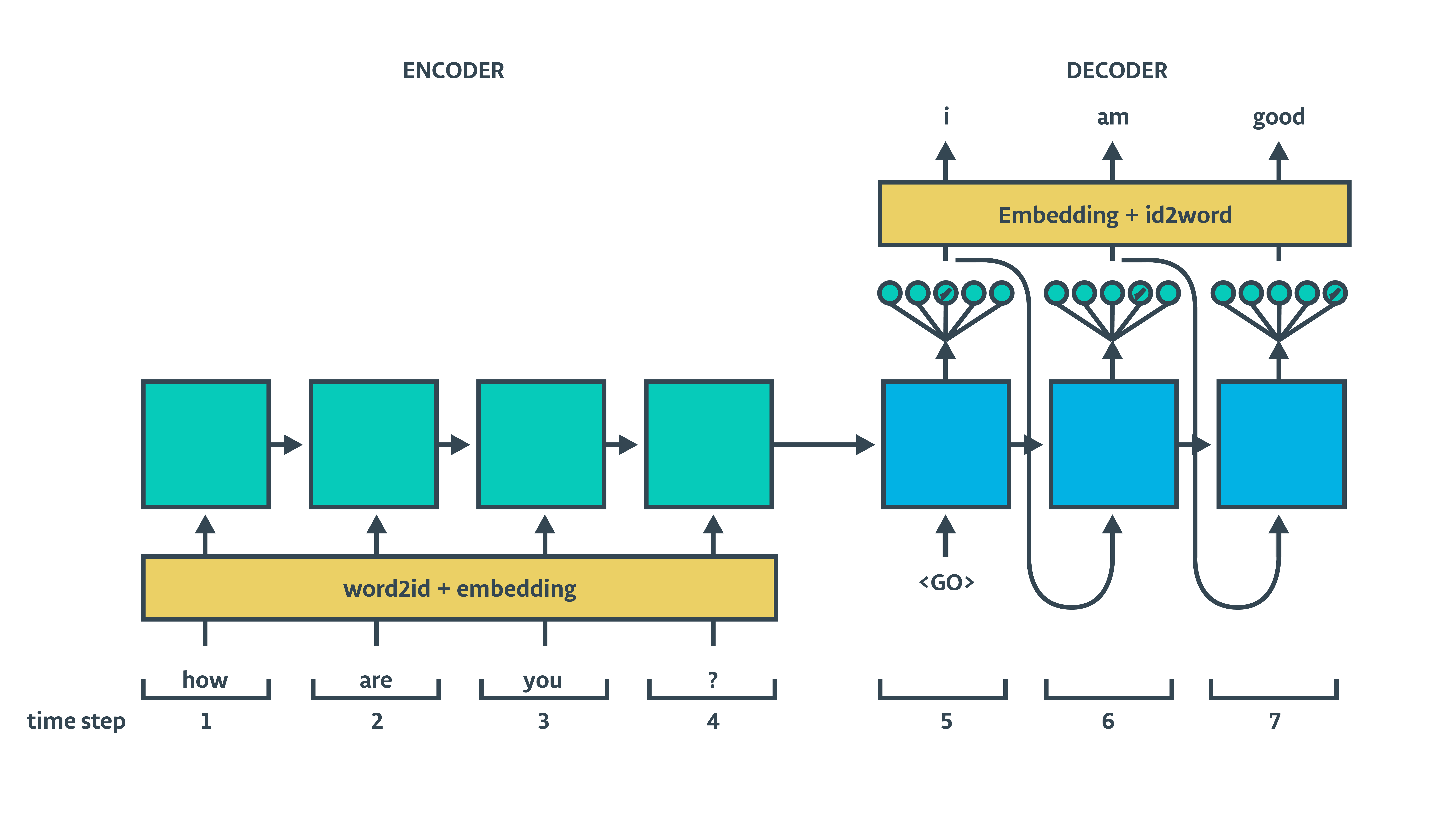 我们会把编码器的隐藏状态喂给训练的和预测用的解码器,让它解码并输出.Tensorflow拥有我们需要的大部分函数.我们只需要 tf.contrib.seq2seq 中合适的函数,还有提供合适的输入.
我们会把编码器的隐藏状态喂给训练的和预测用的解码器,让它解码并输出.Tensorflow拥有我们需要的大部分函数.我们只需要 tf.contrib.seq2seq 中合适的函数,还有提供合适的输入.
代码如下:
def decoding_layer(target_letter_to_int, decoding_embedding_size, num_layers, rnn_size,
target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length, enc_state, dec_input):
# 1. Decoder Embedding
target_vocab_size = len(target_letter_to_int)
dec_embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([target_vocab_size, decoding_embedding_size]))
dec_embed_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(dec_embeddings, dec_input)
# 2. Construct the decoder cell
def make_cell(rnn_size):
dec_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(rnn_size,
initializer=tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.1, 0.1, seed=2))
return dec_cell
dec_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([make_cell(rnn_size) for _ in range(num_layers)])
# 3. Dense layer to translate the decoder's output at each time
# step into a choice from the target vocabulary
output_layer = Dense(target_vocab_size,
kernel_initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean = 0.0, stddev=0.1))
# 4. Set up a training decoder and an inference decoder
# Training Decoder
with tf.variable_scope("decode"):
# Helper for the training process. Used by BasicDecoder to read inputs.
training_helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.TrainingHelper(inputs=dec_embed_input,
sequence_length=target_sequence_length,
time_major=False)
# Basic decoder
training_decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(dec_cell,
training_helper,
enc_state,
output_layer)
# Perform dynamic decoding using the decoder
training_decoder_output = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(training_decoder,
impute_finished=True,
maximum_iterations=max_target_sequence_length)[0]
# 5. Inference Decoder
# Reuses the same parameters trained by the training process
with tf.variable_scope("decode", reuse=True):
start_tokens = tf.tile(tf.constant([target_letter_to_int['<GO>']], dtype=tf.int32), [batch_size], name='start_tokens')
# Helper for the inference process.
inference_helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.GreedyEmbeddingHelper(dec_embeddings,
start_tokens,
target_letter_to_int['<EOS>'])
# Basic decoder
inference_decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(dec_cell,
inference_helper,
enc_state,
output_layer)
# Perform dynamic decoding using the decoder
inference_decoder_output = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(inference_decoder,
impute_finished=True,
maximum_iterations=max_target_sequence_length)[0]
return training_decoder_output, inference_decoder_output
Seq2seq 模型
现在让我们把 编码器 和 解码器 链接起来.
def seq2seq_model(input_data, targets, lr, target_sequence_length,
max_target_sequence_length, source_sequence_length,
source_vocab_size, target_vocab_size,
enc_embedding_size, dec_embedding_size,
rnn_size, num_layers):
# Pass the input data through the encoder. We'll ignore the encoder output, but use the state
_, enc_state = encoding_layer(input_data,
rnn_size,
num_layers,
source_sequence_length,
source_vocab_size,
encoding_embedding_size)
# Prepare the target sequences we'll feed to the decoder in training mode
dec_input = process_decoder_input(targets, target_letter_to_int, batch_size)
# Pass encoder state and decoder inputs to the decoders
training_decoder_output, inference_decoder_output = decoding_layer(target_letter_to_int,
decoding_embedding_size,
num_layers,
rnn_size,
target_sequence_length,
max_target_sequence_length,
enc_state,
dec_input)
return training_decoder_output, inference_decoder_output
解码器的输出都包含一个 ‘rnn_output‘逻辑张量:
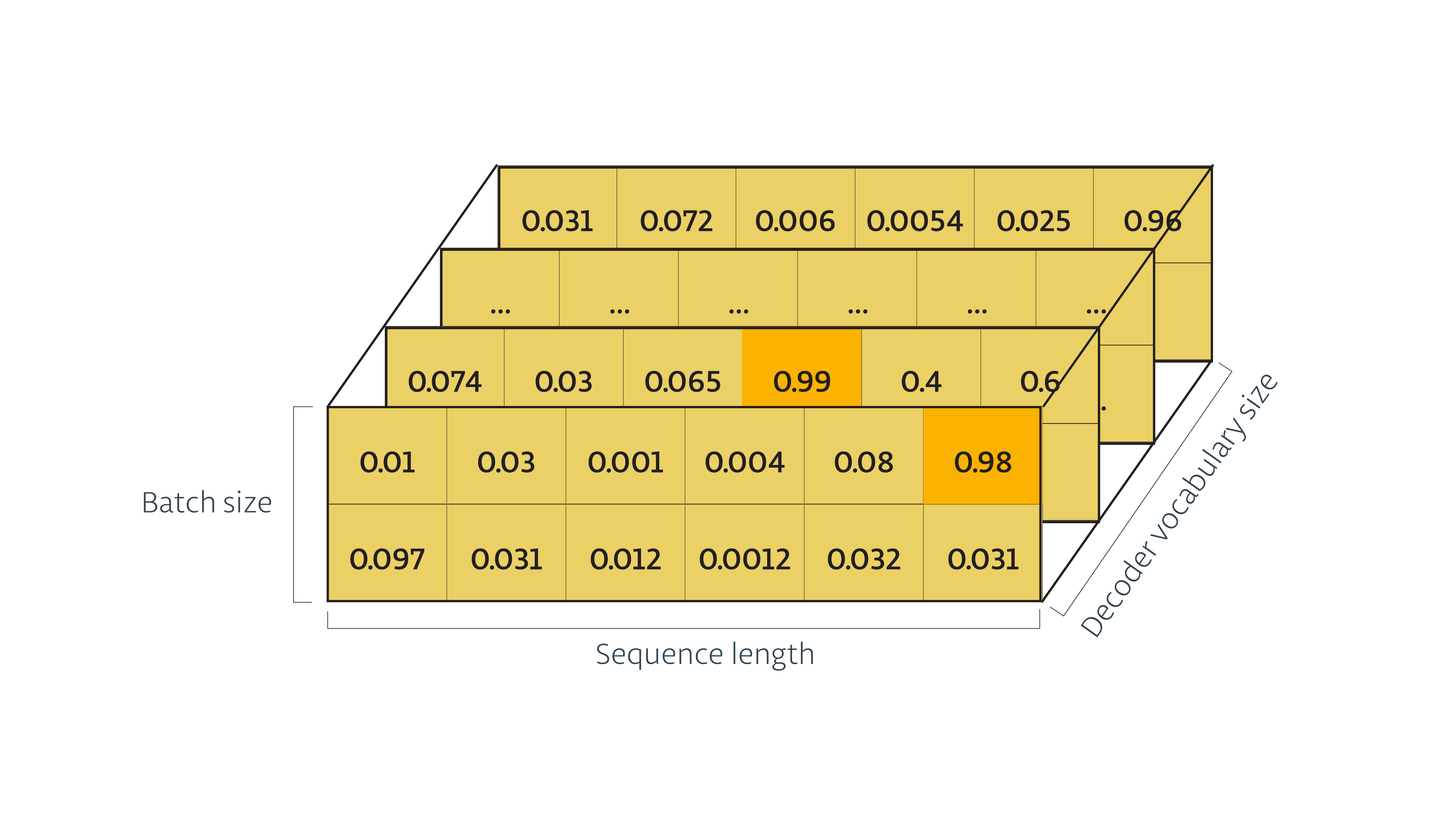 我们将把从训练解码器输出的逻辑张量传给 tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss() 来计算损失和梯度.
我们将把从训练解码器输出的逻辑张量传给 tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss() 来计算损失和梯度.
# Build the graph
train_graph = tf.Graph()
# Set the graph to default to ensure that it is ready for training
with train_graph.as_default():
# Load the model inputs
input_data, targets, lr, target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length, source_sequence_length = get_model_inputs()
# Create the training and inference logits
training_decoder_output, inference_decoder_output = seq2seq_model(input_data,
targets,
lr,
target_sequence_length,
max_target_sequence_length,
source_sequence_length,
len(source_letter_to_int),
len(target_letter_to_int),
encoding_embedding_size,
decoding_embedding_size,
rnn_size,
num_layers)
# Create tensors for the training logits and inference logits
training_logits = tf.identity(training_decoder_output.rnn_output, 'logits')
inference_logits = tf.identity(inference_decoder_output.sample_id, name='predictions')
# Create the weights for sequence_loss
masks = tf.sequence_mask(target_sequence_length, max_target_sequence_length, dtype=tf.float32, name='masks')
with tf.name_scope("optimization"):
# Loss function
cost = tf.contrib.seq2seq.sequence_loss(
training_logits,
targets,
masks)
# Optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr)
# Gradient Clipping
gradients = optimizer.compute_gradients(cost)
capped_gradients = [(tf.clip_by_value(grad, -5., 5.), var) for grad, var in gradients if grad is not None]
train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(capped_gradients)
还有一点值得一提的是每个输入的batch中数组长度需要一致,所以要给数据做适当的填充. 详细训练模型过程,请参考notebook